What Is Chronic Myeloid Leukemia?
Cancer is a medical condition that develops when cells within the body grow out of control. In fact, cells in any part of the body can turn cancerous. The cells spread to other parts of the body.
Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML)
This condition is also referred to as ‘chronic myelogenous leukemia’. It's a type of cancer that starts in certain blood-forming cells of the bone marrow.
CML is common among adults. It is rare among children. Treatment of leukemia for children is
similar to that for adults.
Understanding Leukemia?
Leukemia is a cancer of blood that originates within the blood-forming cells present in the bone marrow. Alteration of one of these cells turns them into a leukemia cell. Rapid proliferation of cells and inability of these cells to die naturally result in excess build-up in the bone marrow which push out normal cells. Sometimes leukemia cells may even exit bone marrow and spill into the bloodstream leading to abnormal increase in white blood cells (WBCs) in the blood, increasing risk of spreading to other organs.
Types of Leukemias may differ. Detection of specific type of leukemia in a patient is helpful for doctors in predicting patient prognosis (outlook). The process is crucial for deciding on a plan the best treatment possible.
What is a chronic leukemia?
Chronic leukemia is a condition where most of the abnormal cells are immature (stem cells) or mature (similar to white blood cells). This condition causes cells to mature only partly. These cells may appear normal but does not function as normal cells do. They are unable to fight infection as well as normal white blood cells do. The leukemia cells also have a tendency to live longer, build up, and overpower normal cells in the bone marrow.
Patients may not experience problems or symptoms with chronic leukemias for a long time. This
also means that patients can live with it for several years. However, chronic leukemias take
longer to treat.
What is a myeloid leukemia?
Leukemia is myeloid depending on the bone marrow cells the cancer starts in. This type of leukemia starts in early myeloid cells, red blood cells, or platelet-making cells.
Other Main Types of Leukemia
Leukemia is generally categorized into 4 major types based on whether they are acute or chronic, and myeloid or lymphocytic. These include:
Diagnosis
Chronic myelogenous leukemia may be detected during a blood test conducted at a lab.
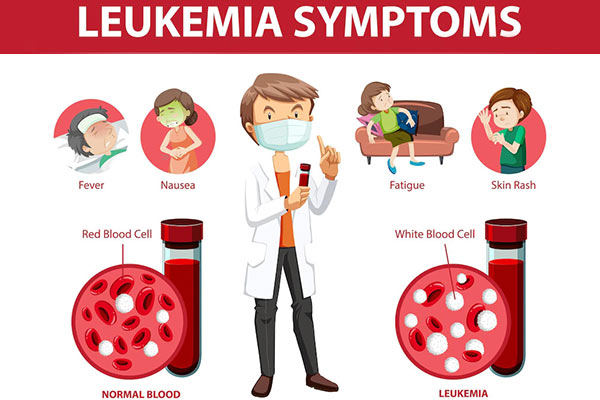
Symptoms of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML)
It is important to keep tabs on any signals body give. If diagnosed early, chronic myeloid leukemia can be cured completely. Here are some main symptoms one can watch out for:
Causes of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
The condition occurs when some unwanted changes happen in the genes of bone marrow cells.
The reason for these changes is not clear.
Generally, human cells contain about 23 pairs of chromosomes holding the DNA that contains instructions (genes) for cell control within body. Individuals with chronic myelogenous leukemia have chromosomes in blood cells which swap sections with each other. A part of chromosome 9 switches places with a section of chromosome 22. The action creates an extra-short chromosome 22 (Philadelphia chromosome present in 90% people with chronic myelogenous leukemia) with an extra-long chromosome 9.
The Philadelphia chromosome creates a new gene while genes from chromosome 9 combine with chromosome 22 genes to further create a new gene called BCR-ABL (instructing abnormal blood cell to produce excess protein referred to as ‘tyrosine kinase’. The protein promotes cancer by allowing rampant certain growth of some blood cells.
The new gene in the blood promotes excess diseased blood cells. Blood cells originate in the bone marrow which normally produces immature cells (blood stem cells) in a controlled way. This process does not work well when an individual develops chronic myelogenous leukemia.
The protein tyrosine kinase caused by the BCR-ABL gene creates white blood cells (most with abnormal Philadelphia chromosome). These unhealthy white blood cells don't grow and die normally. These accumulate in massive numbers force healthy blood cells out and destruct the healthy bone marrow.
Risk factors
Here are some of the risk factors of chronic myelogenous leukemia:
You can take following medicines to get relief from Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: Veenat 100mg, Imatikst 100mg, Dasakast 50mg.
